Observing today’s world can tell us much about tomorrow and what human beings need to meet future challenges. Along with the increasing challenges that we face everyday from economical challenges and climate change to extremism and the increasing language of hate between nations, we should raise a generation that is able to meet these challenges and find innovative solutions for tomorrow’s problems. In a previous article, Can we Apply Design Thinking in Education, we discussed how the current education systems still depend on the some core education pedagogy since decades. Although there is a sustaining innovation in some education systems, these future challenges seek a disruptive innovative that can contribute to building a generation programmed to solve problems rather than dealing with them.
When investigating the different routes to achieve this goal, one route seems to be appealing, as it aims to change how we thinking, which aligns with Albert Einstein’s quote: “You cannot solve a problem with the same mind that created it.” This route is based on design thinking, a methodology that aims to solve problems with a creative approach while putting the user in the center of the process to achieve a user-centered approach. Design thinking processes are not only applied to design business but extend to become a method that can be applied in daily life situation in order to solve our everyday problems or make our lives easier through innovation and creativity.
Why Do We Need Design Thinking?
So, how can this methodology contribute to changing our education system to become more innovation and creativity-biased? While there are different design thinking models—two of which will be discussed later in this article—most of them share the same characteristics while changing the steps and the how the process flows. Some of the characteristics include the following.Highlight problems and curiosity: In the core of the design thinking there is a question to answer or problem to solve. All the design process start with a question that need to be addressed and reaching this question requires an open-mind that is fueled with curiosity to address problems that may not be addressed before.
Collaborative: The process is based on collaborating and sharing ideas and effort among a design thinking team either inside a company or a classroom.
Constructive and holistic: The design process is based on thinking about old ideas with a new approach in order to achieve innovation. Also, it targets a holistic perception for the situation and focuses on the whole system rather than individual elements, similar to systems thinking theory.
Empathic: In order to put the user in the heart of the process, empathy aims to put the team in the shoes of the user of the product or the service. Therefore, they tend to understand their problems, needs, and aims strategies to solve it.
Iterative: The design thinking process depends on appreciating iteration and ongoing improvement through the different steps of the process and even after delivering the final solution.
Nonjudgmental: Developing ideas during the design thinking process depends on a non-judgmental approach. The team freely develops ideas, seeking criticism in order to unleash creativity especially in the ideation and brainstorming phases.
Universal: The design thinking process doesn’t only apply to design; it can be adopted to solve issues in daily life or problems facing any industry.
Design Thinking Models for Education
Although the design thinking process was initially developed for organizations, the above characteristics promote it to become a successful educational method to teach students on different levels about how to think in problems differently and build innovative solutions through chasing their ordinary thinking matrix. Over the course of targeting the education system, two main models were introduced in association with the IDEO, Stanford d.school, and Hasso Plattner Institute of Design. These processes were developed along with local schools and teachers in order to be presented in a form of educational strategy including the process itself, and a number of these activities and tools can be used in school classes.Stanford d.school Design Thinking
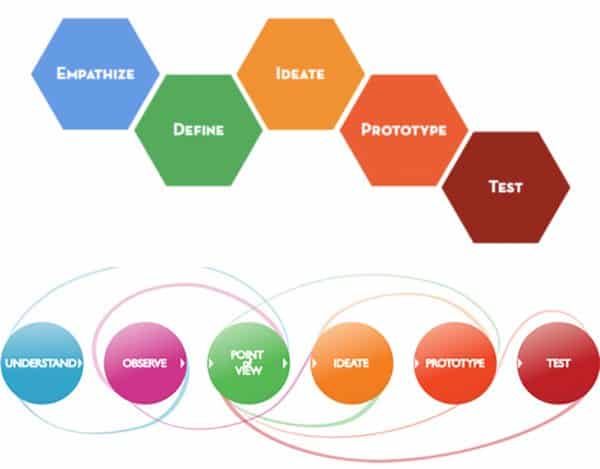
The Stanford d.school design thinking for education model aims to put teachers and students together in hands-on design challenges that focus on building their skills through different design thinking processes. This model depends on the following steps:Empathy: This stage aims to discover the gaps between what people say and do, which will present the question or the opportunity to provide the solution. In this stage, students start by investigating a specific situation or place and how people interact with it.
Define: At this stage, students transform their findings into a description for the situation. This description is the target that needs to be addressed in the following steps.
Ideate: In this stage, students intend to arrive at a solution using any of the design thinking methods such as brainstorming and mind mapping.
Prototype: Students start to build a prototype for the suggested solution. This visual prototype allows them to evaluate the idea and determine whether it meets with the target.
Test: This is the first iteration stage, where the prototype is tested by the students and receives feedback to improve the product to reach a better results.
Iterate: Even after the product is delivered, there should be a process to learn about the current and future experience with the product and to develop the future version of the product.
Note that the above model suggests a continuous iteration process between different stages in order to improve the final product. So, the process may not flow in a linear line, as the iteration process may lead to jumping between processes. Another model was provided with different names for the process: understand, observe, point of view, ideate, prototype, and test.
IDEO Design Thinking for Educators
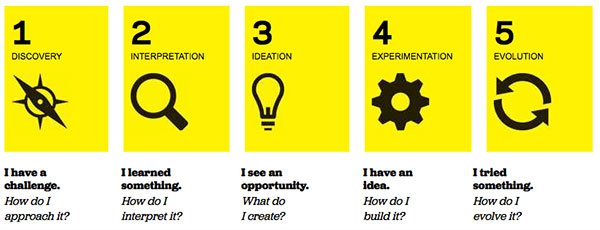
The IDEO mode is introduced on a dedicated website about Design Thinking for Educators, where their toolkit can be downloaded and adopted in classrooms. Similar to the d.school model, this model is based on a process that presents a workflow for educators. It supports a number of in-class activities and tools that help them achieve the target of the design thinking process in education. IDEO model for education is based on five phases.Discovery: This investigation phase intends to build a deep understanding of what is needed and what needs to be solved. This phase gives an understanding to the proposed design challenge.
Interpretation: This phase transforms the collected data or observation into a design opportunity, combining thoughts to form a direction for the ideation phase.
Ideation: This phase is similar to the d.school model. It tends to generate ideas and thinking in different ideas without judgment, criticism, or any constrains.
Experimentation: This phase presents the prototype. Ideas are visualized and turned into a prototype product that can be tested and evaluated.
Evolution: This phase presents the iteration nature of the process, including planning for further development and improving the ideas.
Resources for Design Thinking Educators and References
Design thinking for education resources are available online in different domains that can help educators and school administrators to directly put this approach into action. The following are some resources that can be downloaded and used in class or to build a class system based on design thinking:- IDEO Design Thinking for Educators website
- Stanford Educator Guide to Design Thinking
- Taking Design Thinking to Schools
- Introduction to Design Thinking
- IDEO Design Thinking Kit
- Change by Design, a book by Tim Brown
- Make Space: How to Set the Stage for Creative Collaboration, a book by Scott Doorley, Scott Witthoft, Hassor Plattner Institute of Design, and Stanford University
Using design thinking as a teaching method helps our students to become more empathic, collaborative, and open-minded. They can solve problems regardless of the industry they will work in when they join the workforce. While there are different design thinking methods, the Stanford d.school and IDEO design thinking methods were introduced along with a set of tools and activities that educators can implement directly into their classes. This approach can help schools directly adopt a creative thinking model, which may change students’ thinking to a more creative and innovative approach, resulting in a new generation geared toward solving world problems instead of making them.